backscatter rf tag Backscatter is a method of communication in which an RFID tagwithout a battery (or any internal power source) receives energy from an RFID . See more The most recent development in the field of hotel key cards is the use of NFC enabled mobile phones. Visitors can unlock their room doors through their smartphones by enabling the NFC feature and bringing their phones in close .
0 · what is backscatter
1 · how to explain backscatter
2 · backscatter vs magnetic
3 · backscatter reverse link
4 · backscatter frequency
Near Field Communication (NFC) is contactless transfer technology similar to Bluetooth and Wi .The Bolt Card. On 17th May, we announced The Bolt Card - the world’s first contactless Bitcoin Lightning card. “Using a standard NFC card, the Lightning Network and LNURL, The Bolt Card enables a user to simply tap their card on .
what is backscatter
This article walks through the basics and advanced principles related to how UHF RFID Passive tags communicate via backscatter. Before reading, it is important to know about the types of coupling and when each one is used. If you do not know what coupling is and how it works, please refer to " Principles of . See more
Backscatter is a method of communication in which an RFID tagwithout a battery (or any internal power source) receives energy from an RFID . See moreFor more information on RFID, comment below or contact us! If you would like to learn more about all things RFID, check out our website or our YouTube channel. To read more about . See moreWhen diving deeper into backscatter, it is impossible to leave out the presence and use of an electric field versus exclusively using a magnetic field. The three most used frequencies for RFIDare Low-Frequency (LF), High-Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High . See more
i band 3 nfc
how to explain backscatter
In backscatter communication systems, a power-constrained wireless device piggybacks its data on ambient wireless signals instead of generating its own radio frequency .
Backscatter is a method of communication in which an RFID tag without a battery (or any internal power source) receives energy from an RFID reader’s transmission and uses that same energy to send back a reply. The tag receives the energy via electromagnetic waves propagated from the reader/antenna. In backscatter communication systems, a power-constrained wireless device piggybacks its data on ambient wireless signals instead of generating its own radio frequency (RF) waves, which would. In the past two decades, point-to-point BackCom has been widely deployed in the application of radio-frequency identification (RFID) for a passive RFID tag to report an ID to an enquiring Reader over the near field (typically several centimeters). This paper presents a 5.8-GHz RFID tag that, by exploiting the quantum tunneling effect, significantly increases the range of backscatter radio links. We present an electronically simple Tunneling RFID Tag characterized by return gains as high as 35 dB with link sensitivity as low as -81 dBm.
Abstract: The interest in wearable antenna design has increased significantly due to its potential applications for humans, especially in the context of RF identification (RFID) technology. RFID transponders can wirelessly transmit identification numbers or sensor data over short distances.
This paper studies tag properties for optimized tag-to-reader backscatter communication. The latter is exploited in RF identification (RFID) systems and utilizes binary reflection coefficient change of the tag antenna-load circuit. Backscattering tags transmit passively without an on-board active radio transmitter. Almost all present-day backscatter systems, however, rely on active radio receivers. This presents a significant scalability, power and cost challenge for backscatter systems. The backscatter radio system allows passive tags to consume sufficient energy from incident RF carrier signals, generated by different sources, while reflecting back part of the carrier signals to transmit the tag’s data .
We propose to leverage the deployment of LiFi networks built upon LED bulbs for pervasive RF backscatter. We experimentally demonstrate that LiFi, which passively leaks RF signals, can be exploited as a radio carrier generator for low-power RF backscatter.This work promises to enable low-powered wireless sensors and a new-generation of RFID applications. A retrodirective RF tag reflects and modulates incident radio waves back in the direction of transmission, much like a corner-reflector in optics. Backscatter is a method of communication in which an RFID tag without a battery (or any internal power source) receives energy from an RFID reader’s transmission and uses that same energy to send back a reply. The tag receives the energy via electromagnetic waves propagated from the reader/antenna.
mi 3 band nfc
In backscatter communication systems, a power-constrained wireless device piggybacks its data on ambient wireless signals instead of generating its own radio frequency (RF) waves, which would.
In the past two decades, point-to-point BackCom has been widely deployed in the application of radio-frequency identification (RFID) for a passive RFID tag to report an ID to an enquiring Reader over the near field (typically several centimeters).
This paper presents a 5.8-GHz RFID tag that, by exploiting the quantum tunneling effect, significantly increases the range of backscatter radio links. We present an electronically simple Tunneling RFID Tag characterized by return gains as high as 35 dB with link sensitivity as low as -81 dBm.
Abstract: The interest in wearable antenna design has increased significantly due to its potential applications for humans, especially in the context of RF identification (RFID) technology. RFID transponders can wirelessly transmit identification numbers or sensor data over short distances. This paper studies tag properties for optimized tag-to-reader backscatter communication. The latter is exploited in RF identification (RFID) systems and utilizes binary reflection coefficient change of the tag antenna-load circuit. Backscattering tags transmit passively without an on-board active radio transmitter. Almost all present-day backscatter systems, however, rely on active radio receivers. This presents a significant scalability, power and cost challenge for backscatter systems. The backscatter radio system allows passive tags to consume sufficient energy from incident RF carrier signals, generated by different sources, while reflecting back part of the carrier signals to transmit the tag’s data .
We propose to leverage the deployment of LiFi networks built upon LED bulbs for pervasive RF backscatter. We experimentally demonstrate that LiFi, which passively leaks RF signals, can be exploited as a radio carrier generator for low-power RF backscatter.
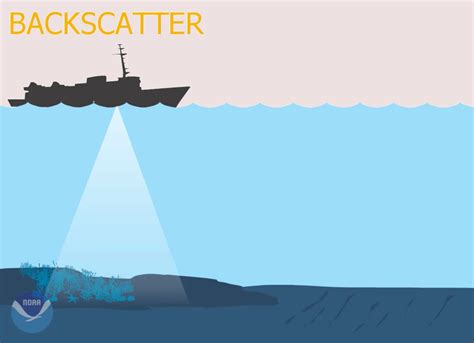
backscatter vs magnetic
Any card that you request from Barclays comes with Contactless (the ability to tap your card .
backscatter rf tag|backscatter frequency