rfid reader vs nfc reader RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency. Tiger 95.9 WTGZ FM is the premiere alternative music radio station based in Auburn, Alabama. Tiger 95.9 FM is home to SportsCall from 4-6pmCT weekdays. English; site; Like 1 Listen live 0. Contacts; The Tiger 95.9 FM reviews. .
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid nfc reader writer
2 · nfc tag reader used for
3 · nfc rfid reader software
4 · nfc rfid reader app
5 · differences between rfid and nfc
6 · adafruit rfid reader
7 · adafruit nfc reader
Auburn football radio announcers. Andy Burcham is the "Voice of the Tigers" on the radio. He serves as a play-by-play announcer for baseball and men's basketball as well. .
RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency . RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, .
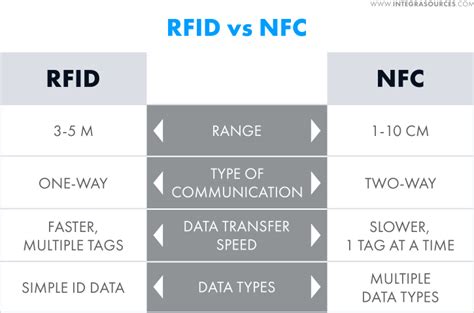
RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency systems can range 25 feet or more. RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in .One of the main differences between RFID and NFC is their reading range. Depending on the operating frequency, the reading range of RFID technology can be extended from a few centimeters to more than ten meters. Compared to RFID, the .
NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.
NFC vs. RFID: How to Choose. When choosing NFC vs. RFID technology, you need to consider the following key factors: Reading distance. If the application scenario requires close-range data exchange, such as payment or access control, NFC is an ideal choice.
RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.In peer-to-peer mode, two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data directly, without the need for a central server or intermediary. In reader/writer mode, the NFC device can read and write data to NFC tags, similar to how an RFID reader interacts with .
However, there is a distinction between the two. Unlike RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags, NFC tags have the capability to both send and receive information, allowing for two-way communication. In contrast, RFID tags are typically designed for one-way communication. RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency systems can range 25 feet or more.
RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in .One of the main differences between RFID and NFC is their reading range. Depending on the operating frequency, the reading range of RFID technology can be extended from a few centimeters to more than ten meters. Compared to RFID, the .
NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.NFC vs. RFID: How to Choose. When choosing NFC vs. RFID technology, you need to consider the following key factors: Reading distance. If the application scenario requires close-range data exchange, such as payment or access control, NFC is an ideal choice.
RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.
rfid vs nfc difference
In peer-to-peer mode, two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data directly, without the need for a central server or intermediary. In reader/writer mode, the NFC device can read and write data to NFC tags, similar to how an RFID reader interacts with .
mini tags rfid
mifare ultralight rfid ubisoft battle tag

Nothing beats a Saturday listening to Auburn Sports Network’s all-day coverage of Auburn Tigers football in the fall. This season’s lineup within the Auburn Sports Network changes slightly, as Andy Burcham will be joined by .
rfid reader vs nfc reader|differences between rfid and nfc