physical architecture rfid waste smart system In this paper, we outline a RFID and sensor model for designing a system in real . CALL THE SHOW AT 866.WE.BE.BIG. Listen Live! wATCH Live!
0 · intelligent waste management system pdf
1 · intelligent waste management
The answer is quite simple: all you have to do is tap your iPhone to another device that’s NFC-enabled. Or simply hold the top back of your iPhone close to an NFC tag. Then, the iPhone reads the NFC tag and displays a .
intelligent waste management system pdf
smart card on gnome
intelligent waste management
A dynamic waste management system is presented as an online deduction process that is . In this paper, we outline a RFID and sensor model for designing a system in real . Smart waste management (SWM) involves for example collection and analytics of .
This paper presents an intelligent waste management system (IWMS) in smart .A dynamic waste management system is presented as an online deduction process that is used to decide when trucks should collect waste from smart bins in a source building and to determine the optimum paths that the collection trucks should use. In this paper, we outline a RFID and sensor model for designing a system in real-time waste management. An application of the architecture is described in the area of RFID and sensor based automatic waste identity, weight, and stolen bins identification system (WIWSBIS).
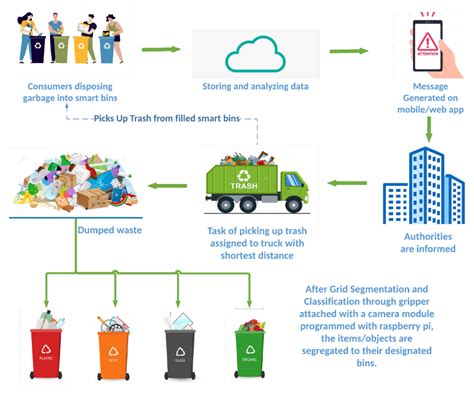
Smart waste management (SWM) involves for example collection and analytics of data from sensors on smart garbage bins (SGBs), management of waste trucks and urban infrastructure; planning and optimization of waste truck routes; etc. This paper presents an intelligent waste management system (IWMS) in smart cities based on Internet of Things components like sensors, detectors, and actuators. IWMS contains three main phases.
smart card ok
With the use of sensors, radiofrequency (RFID) and actuators in the process of monitoring identification, this set is divided into three phases: (i) Planning and execution of waste collection using solutions of routing in trucks with dynamic adaptation of routes according to restrictions introduced; (ii) transport to a specific place according . This work proposes an IoT-enabled solid waste management system for smart cities to overcome the limitations of the traditional waste management systems. The proposed architecture consists of two types of end sensor nodes: PBLMU (Public Bin Level Monitoring Unit) and HBLMU (Home Bin Level Monitoring Unit), which are used to track bins in public . The aim of this paper was to present the architecture of a Smart Waste Management infrastructure based on the LoRaWAN transmission technology, going beyond the single-purpose operation of a wide range of solutions that are currently found in the literature.Abstract: This work presents the architecture, modelling, simulation, and physical implementation of a versatile, scalable system for use in common-type waste-bins that can perform and transmit accurate fill-level estimates while consuming minimal power and consisting of low-cost embedded components. The sensing units are based on ultrasonic .

Smart waste management (SWM) involves for example collection and analytics of data from sensors on smart garbage bins (SGBs), management of waste trucks and urban infrastructure; planning. A Series of literature have been examined in this paper specially focused on the physical infrastructure of waste bins using IoT technology for an efficient waste management system. The comparative evaluation of this study is depicted in Table 1 .A dynamic waste management system is presented as an online deduction process that is used to decide when trucks should collect waste from smart bins in a source building and to determine the optimum paths that the collection trucks should use.
In this paper, we outline a RFID and sensor model for designing a system in real-time waste management. An application of the architecture is described in the area of RFID and sensor based automatic waste identity, weight, and stolen bins identification system (WIWSBIS).
Smart waste management (SWM) involves for example collection and analytics of data from sensors on smart garbage bins (SGBs), management of waste trucks and urban infrastructure; planning and optimization of waste truck routes; etc.
This paper presents an intelligent waste management system (IWMS) in smart cities based on Internet of Things components like sensors, detectors, and actuators. IWMS contains three main phases.
With the use of sensors, radiofrequency (RFID) and actuators in the process of monitoring identification, this set is divided into three phases: (i) Planning and execution of waste collection using solutions of routing in trucks with dynamic adaptation of routes according to restrictions introduced; (ii) transport to a specific place according .
This work proposes an IoT-enabled solid waste management system for smart cities to overcome the limitations of the traditional waste management systems. The proposed architecture consists of two types of end sensor nodes: PBLMU (Public Bin Level Monitoring Unit) and HBLMU (Home Bin Level Monitoring Unit), which are used to track bins in public . The aim of this paper was to present the architecture of a Smart Waste Management infrastructure based on the LoRaWAN transmission technology, going beyond the single-purpose operation of a wide range of solutions that are currently found in the literature.Abstract: This work presents the architecture, modelling, simulation, and physical implementation of a versatile, scalable system for use in common-type waste-bins that can perform and transmit accurate fill-level estimates while consuming minimal power and consisting of low-cost embedded components. The sensing units are based on ultrasonic . Smart waste management (SWM) involves for example collection and analytics of data from sensors on smart garbage bins (SGBs), management of waste trucks and urban infrastructure; planning.
The NFC Reader Wave ID® Nano by rf IDEAS is equipped with USB-C and meets Military Standard MIL-STD-810. Can read any type of NFC Cards. No drivers required.
physical architecture rfid waste smart system|intelligent waste management