nfc rifd tags Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from . This app emulates an NFC Forum Type 4 Tag on an Android device using Host-based Card Emulation ("HCE").. To be compliant with the specification a service is running independent on the app opened that serves an Application Identifier .
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid tags pros and cons
2 · pros and cons of nfc
3 · nfc tags are always passive
4 · nfc disadvantages
5 · different types of rfid tags
6 · differences between rfid and nfc
7 · are nfc tags waterproof
Cloning Mifare NFC cards with a mobile phone # Although the BlackHat guide worked well, it can be a bit frustrating to use since you have to get some components together and hack away at a guide for an hour or two to .The latest update is all about RFID and NFC, and how the Flipper Zero can .
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency .
Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from .
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed .Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that enables the sharing of data encoded in RFID tags via RFID scanners. The term RAIN RFID specifies use of the UHF frequency band, which leverages the GS1® air interface protocol to communicate with tags.
However, NFC tags can store up to 4KB of data, which can be in a variety of formats, including text, URLs, and media. In contrast, RFID tags have a much wider range of storage capacity, from a few bytes to several kilobytes, and are capable of storing much more tracking information and data. Short Answer: RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency. Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags are a broad category of smart labels encompassing near field communication (NFC) tags, ultra-high-frequency (UHF) tags and more. If you’re considering deploying an RFID solution, it’s important to understand the differences between each RFID type and partner with a pressure-sensitive label .Shop NFC tags from major brands including Avery Dennison, Confidex, Beontag and more . Browse the best NFC tags in one place. Save 5% instantly w/ a free Atlas+ account. FREE shipping on 0+ U.S. orders.
rfid vs nfc difference
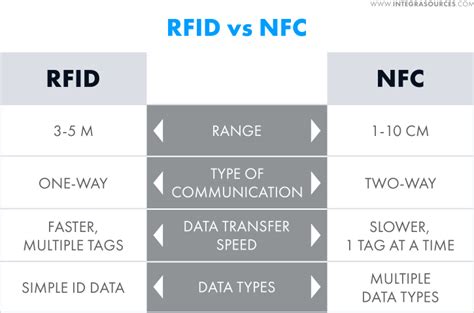
RFID and NFC systems use short-range communication to read the ID information on tags. They find use in many spheres of life: contactless payment transactions, asset tracking, real time location systems, access control, retail, marketing, and more.RFID’s ultra-high frequency technology can read multiple tags in batches at a long distance, greatly improving the efficiency of logistics and inventory management, while NFC is not suitable for large-scale tracking applications due to its short communication distance. Unlike RFID tags, only one tag can be read at a time with NFC technology. This can limit its use cases and means that RFID tags are often better suited to environments where there are a lot of trackable components.
rfid tags pros and cons
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed .
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that enables the sharing of data encoded in RFID tags via RFID scanners. The term RAIN RFID specifies use of the UHF frequency band, which leverages the GS1® air interface protocol to communicate with tags. However, NFC tags can store up to 4KB of data, which can be in a variety of formats, including text, URLs, and media. In contrast, RFID tags have a much wider range of storage capacity, from a few bytes to several kilobytes, and are capable of storing much more tracking information and data.
Short Answer: RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency. Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags are a broad category of smart labels encompassing near field communication (NFC) tags, ultra-high-frequency (UHF) tags and more. If you’re considering deploying an RFID solution, it’s important to understand the differences between each RFID type and partner with a pressure-sensitive label .Shop NFC tags from major brands including Avery Dennison, Confidex, Beontag and more . Browse the best NFC tags in one place. Save 5% instantly w/ a free Atlas+ account. FREE shipping on 0+ U.S. orders.
RFID and NFC systems use short-range communication to read the ID information on tags. They find use in many spheres of life: contactless payment transactions, asset tracking, real time location systems, access control, retail, marketing, and more.RFID’s ultra-high frequency technology can read multiple tags in batches at a long distance, greatly improving the efficiency of logistics and inventory management, while NFC is not suitable for large-scale tracking applications due to its short communication distance.
how to use nfc cards in breath of the wild
pros and cons of nfc
In a nutshell, the Micro SIM and Nano SIM are essentially the same thing, differing only in their sizes – in this case, bigger is not always better. Both the Micro SIM and the Nano SIM are defined by their form factors, with .
nfc rifd tags|rfid vs nfc difference