uhf active rfid noise immunity This paper presents a novel signal demodulator for ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag chips. It has the advantages of high noise immunity, large input range and low power consumption. PS: If you having issues with the NFC Tag not reading, make sure you have your scheme set to vnd.android.nfc in your Manifest. android:scheme=”vnd.android.nfc” For a more .
0 · Recent Advances and Applications of Passive Harmonic RFID
1 · Adaptive Noise
RFID tags can be as small as a few centimeters in size and can be placed in an object or its packaging to receive communication radio waves. A complete system using RFID tags consists of four parts: the tag, an antenna, a reader, and a .
This paper presents a new signal demodulator for ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag chips. The demodulator is used to demodulate amplitude shift keying (ASK) modulated signals with the advantages of high noise immunity, large input range . This paper presents a novel signal demodulator for ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag chips. It has the advantages of high noise immunity, .
Harmonic RFID is desired over conventional RFID systems due to reduced self-jamming, location accuracy from dual frequency, and higher phase noise immunity. In a . This paper presents a new signal demodulator for ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag chips. The demodulator is used to demodulate amplitude shift keying (ASK) modulated signals with the advantages of high noise immunity, large input range and low power consumption. This paper presents a novel signal demodulator for ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag chips. It has the advantages of high noise immunity, large input range and low power consumption.
Harmonic RFID is desired over conventional RFID systems due to reduced self-jamming, location accuracy from dual frequency, and higher phase noise immunity. In a harmonic RFID system, the tag receives instructions from the reader at an RF carrier frequency and replies back at the harmonic of the RF frequency.This paper investigates the effects of RF interference be-tween a passive UHF RFID system and a communications sys-tem sharing the 902 MHz to 928 MHz industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) band. This paper presents a new signal demodulator for ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag chips. The demodulator is used to demodulate amplitude shift keying (ASK).
Using an RFID system allows consolidated management of objects and information. Purposes of using RFID in a production site mainly comprises the following applications. Work instruction (destination instruction) History management (production history, work .The demodulator also has a noise immunity threshold of approximately 3.729 V. Keywords:ASK; demodulator; RFID; hysteresis of input; differential operational amplifier. 1. Introduction. The. Flexible antennas with compact dimensions and reasonable gain are necessary for UHF-RFID tags, but other components, including an RFIC, matching network, and sensors are needed to create an.
In this work, we demonstrate that it is possible to read UHF RFID tags without a carrier. Specifically, we introduce an alternative reader design that does not emit a carrier and allows reading RFID tags intended for conventional carrier-based systems.
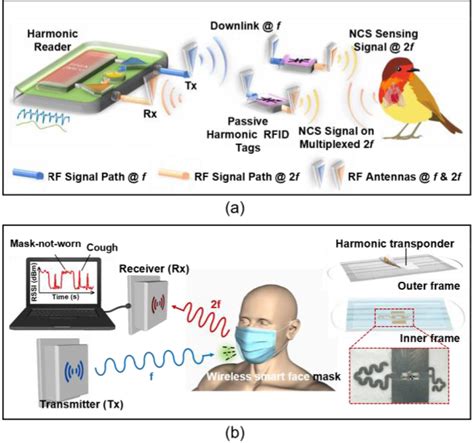
Recent Advances and Applications of Passive Harmonic RFID
Especially in ultra-high frequency (UHF) RF identification (RFID) systems noise plays and important role. This is because the noise performance of the receiver chain is defined not only by the intrinsic noise of the receiver, but also by the large self-jammer signal. This paper presents a new signal demodulator for ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag chips. The demodulator is used to demodulate amplitude shift keying (ASK) modulated signals with the advantages of high noise immunity, large input range and low power consumption. This paper presents a novel signal demodulator for ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag chips. It has the advantages of high noise immunity, large input range and low power consumption. Harmonic RFID is desired over conventional RFID systems due to reduced self-jamming, location accuracy from dual frequency, and higher phase noise immunity. In a harmonic RFID system, the tag receives instructions from the reader at an RF carrier frequency and replies back at the harmonic of the RF frequency.
This paper investigates the effects of RF interference be-tween a passive UHF RFID system and a communications sys-tem sharing the 902 MHz to 928 MHz industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) band. This paper presents a new signal demodulator for ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag chips. The demodulator is used to demodulate amplitude shift keying (ASK).
Using an RFID system allows consolidated management of objects and information. Purposes of using RFID in a production site mainly comprises the following applications. Work instruction (destination instruction) History management (production history, work .
The demodulator also has a noise immunity threshold of approximately 3.729 V. Keywords:ASK; demodulator; RFID; hysteresis of input; differential operational amplifier. 1. Introduction. The. Flexible antennas with compact dimensions and reasonable gain are necessary for UHF-RFID tags, but other components, including an RFIC, matching network, and sensors are needed to create an.In this work, we demonstrate that it is possible to read UHF RFID tags without a carrier. Specifically, we introduce an alternative reader design that does not emit a carrier and allows reading RFID tags intended for conventional carrier-based systems.
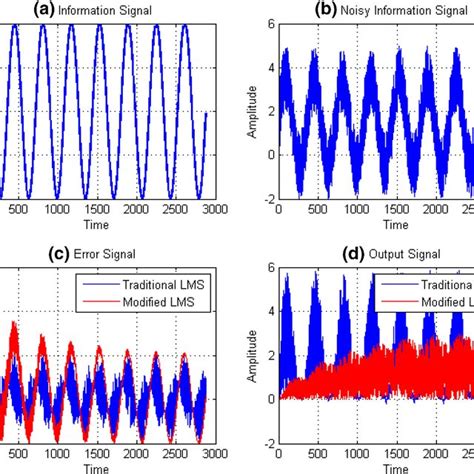
Adaptive Noise
Step 1: Open the Shortcuts app > go to the Automation tab. Step 2: Tap New Automation or + (from the top-right corner). Step 3: Here, scroll down or search for NFC. Tap it. Step 4: Tap Scan. Hold .
uhf active rfid noise immunity|Recent Advances and Applications of Passive Harmonic RFID