nfc as rfid reader As you just read, NFC duplicates RFID's feat by reading smart tags, thanks to its read/write operation mode. But in addition to read/write . In order to access the cards, you must following two steps: 'Connect' to a Mifare Ultralight card and retrieve the 7 byte UID of the card. Memory can be read and written directly once a .NFC Tools Online. NFC Tools Online. NDEF NFC Tag Reader Write Text to NFC Tag Write URL to NFC Tag Write WiFi to NFC Tag Write Android App Text to NFC Tag. Online tools to read and write the data on your NFC tags.
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid nfc reader writer
2 · nfc tag reader used for
3 · nfc rfid reader software
4 · nfc rfid reader app
5 · differences between rfid and nfc
6 · adafruit rfid reader
7 · adafruit nfc reader
Toys & Collectibles New Finds. Sporting Goods New Finds. Travel & Hobby New Finds. .
Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed temperature, vibration or . As you just read, NFC duplicates RFID's feat by reading smart tags, thanks to its read/write operation mode. But in addition to read/write . Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed .As you just read, NFC duplicates RFID's feat by reading smart tags, thanks to its read/write operation mode. But in addition to read/write capabilities, NFC has two other modes, both of which involve dynamic, two-way communication: card emulation and P2P (peer-to-peer).
When it comes down to it, NFC is a type of RFID. So, while all NFC is considered RFID, not all RFID is NFC. Let’s compare the two, side by side, to better understand where they overlap and what makes them different.
NFC tags contain data and tend to be read-only. These tags can securely hold personal data, with memory ranging between 96 and 8,192 bytes. As with RFID technology, . RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.RFID’s ultra-high frequency technology can read multiple tags in batches at a long distance, greatly improving the efficiency of logistics and inventory management, while NFC is not suitable for large-scale tracking applications due to its short communication distance.NFC excels in short-range communication, contactless transactions, and device pairing, offering two-way communication and enhanced security. On the other hand, RFID operates over longer distances, reads multiple tags simultaneously, and is commonly used for object identification, tracking, and inventory management.
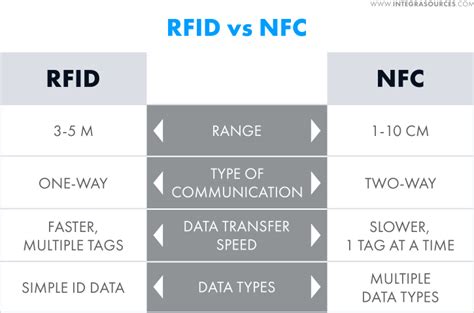
NFC is a special form of high-frequency RFID technology, and its operating frequency is usually maintained in the 13.56 MHz band. In addition, the reading distance of NFC technology is relatively short, generally within 10 centimeters.RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a non-physical technique used to relay information. It relies on smart tags, which are attached to objects like products in stores or animals on a farm. The smart tags work in collaboration with RFID readers, which provide power and receive the relayed identification data. Supply chain uses for RFID include using RFID readers to get information from tags on individual products or shipping containers. In addition, smart tags can track environmental conditions for product boxes and record when products exceed .
playoff standings nfc
As you just read, NFC duplicates RFID's feat by reading smart tags, thanks to its read/write operation mode. But in addition to read/write capabilities, NFC has two other modes, both of which involve dynamic, two-way communication: card emulation and P2P (peer-to-peer).When it comes down to it, NFC is a type of RFID. So, while all NFC is considered RFID, not all RFID is NFC. Let’s compare the two, side by side, to better understand where they overlap and what makes them different. NFC tags contain data and tend to be read-only. These tags can securely hold personal data, with memory ranging between 96 and 8,192 bytes. As with RFID technology, .
RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.RFID’s ultra-high frequency technology can read multiple tags in batches at a long distance, greatly improving the efficiency of logistics and inventory management, while NFC is not suitable for large-scale tracking applications due to its short communication distance.NFC excels in short-range communication, contactless transactions, and device pairing, offering two-way communication and enhanced security. On the other hand, RFID operates over longer distances, reads multiple tags simultaneously, and is commonly used for object identification, tracking, and inventory management.
NFC is a special form of high-frequency RFID technology, and its operating frequency is usually maintained in the 13.56 MHz band. In addition, the reading distance of NFC technology is relatively short, generally within 10 centimeters.
RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally.
rfid vs nfc difference
rfid nfc reader writer
nfc playoff standings as of today
This is NFC reader app. Safety starts with understanding how developers .Hunter Cat NFC can be set to behave either as an NFC reader, a tag, or to establish a two-way .
nfc as rfid reader|differences between rfid and nfc