passive rfid tag harvests Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The . TIGER TALK. Thursdays at 6 p.m. CT. Hosted by Brad Law and the Voice of .
0 · What Are Passive RFID Tags? How They Work and Uses
1 · Printed, flexible, compact UHF
2 · Active vs. Passive RFID Tags: Understanding the Difference
3 · Active RFID vs. Passive RFID: What’s the Difference?
4 · A Designers Guide to RFID
Sensa Pens: The Other Type Of Pens Like You Don't See Them Around Anywhere Else http://goo.gl/9UaAIx Auburn radio call - final play of the 2013 Alabama @ Aub.
We developed a screen-printed, flexible, wireless temperature sensor tag using passive UHF RFID using printed, flexible dipole antennas.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The . We developed a screen-printed, flexible, wireless temperature sensor tag using passive UHF RFID using printed, flexible dipole antennas.
Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader.
Discover the essentials of RFID passive tags, including their advantages, applications, and limitations. Learn how modern technology addresses these challenges and helps you make informed decisions for your RFID needs. By comparison, passive RFID tags work by reflecting and re-modulating a strong radio signal from a sophisticated reader, which dissipates in strength. This can correlate to a reduction in range, which could limit some use cases based on read distance required. . First, ambient IoT harvests the radio energy it needs over time. This means it .This paper proposes an energy harvesting system for passive Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags which operate in ultra high frequency band by utilizing the power carried by harmonics of the chip signal.
The reported findings hold an excellent promise for R.F energy harvesting and utilisation, adaptive intelligent energy-efficient data communication, and seamless, ubiquitous.
This paper presents a novel approach for incorporating solar harvesting capability into existing passive RFID tags without increasing the parts count or changing the tag assembly process. In this paper we present the architecture of a passive sensor tag that harvests RF power from a 200 mW reader base station operating at 430 MHz. The tag is well suited for structural health monitoring (SHM) applications of large engineering structures such as bridges, naval ships etc. This paper introduces a relevant concept of energy harvesting for passive UHF radio frequency identification (RFID) relying on the exploitation of the power carried by the third harmonic signal generated by the RFID chip. We are making durable passive RFID sensor tags that work using standard UHF frequencies and do not sacrifice read range. Passive sensor tags are primarily a chip and antenna; the chip’s integrated circuit harvests energy from the UHF reader to transmit changing antenna impedance correlated to pressure, temperature or moisture level.
We developed a screen-printed, flexible, wireless temperature sensor tag using passive UHF RFID using printed, flexible dipole antennas.Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader.Discover the essentials of RFID passive tags, including their advantages, applications, and limitations. Learn how modern technology addresses these challenges and helps you make informed decisions for your RFID needs. By comparison, passive RFID tags work by reflecting and re-modulating a strong radio signal from a sophisticated reader, which dissipates in strength. This can correlate to a reduction in range, which could limit some use cases based on read distance required. . First, ambient IoT harvests the radio energy it needs over time. This means it .
This paper proposes an energy harvesting system for passive Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags which operate in ultra high frequency band by utilizing the power carried by harmonics of the chip signal.
What Are Passive RFID Tags? How They Work and Uses
Printed, flexible, compact UHF


The reported findings hold an excellent promise for R.F energy harvesting and utilisation, adaptive intelligent energy-efficient data communication, and seamless, ubiquitous.
This paper presents a novel approach for incorporating solar harvesting capability into existing passive RFID tags without increasing the parts count or changing the tag assembly process.
In this paper we present the architecture of a passive sensor tag that harvests RF power from a 200 mW reader base station operating at 430 MHz. The tag is well suited for structural health monitoring (SHM) applications of large engineering structures such as bridges, naval ships etc.
This paper introduces a relevant concept of energy harvesting for passive UHF radio frequency identification (RFID) relying on the exploitation of the power carried by the third harmonic signal generated by the RFID chip.
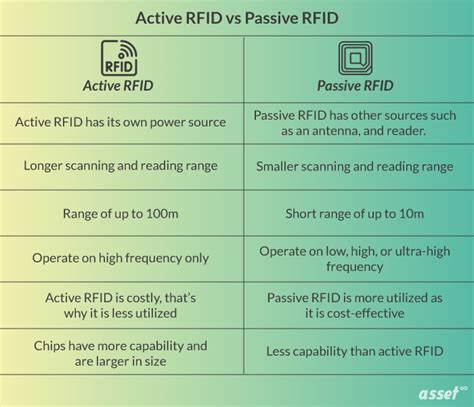
Active vs. Passive RFID Tags: Understanding the Difference
Active RFID vs. Passive RFID: What’s the Difference?
Member Auburn Chamber of Commerce, Opelika Chamber of Commerce, Alabama Broadcasters Association, and National Association of Broadcasters. . The Federal Communications Commission’s Foreign Sponsorship Disclosure .
passive rfid tag harvests|Active RFID vs. Passive RFID: What’s the Difference?