rfid tag epc tid The main difference between EPC and TID is that EPC contains unique information about the products while TID gives a unique identification to each RFID tag. Get the best deals for Nfc Reader at eBay.com. We have a great online selection at the lowest .
0 · what is epc in rfid
1 · what is epc data
2 · epcglobal gen2
3 · epc rfid gen 3
4 · epc gen 2 rfid
5 · epc codes lookup
6 · epc barcode
7 · decode identifier
$18.99
what is epc in rfid
In RFID technology, EPC (Electronic Product Code) and TID (Tag Identifier) are two core concepts. For companies that want to choose and use RFID technology, an in-depth understanding of these two elements will help them more accurately customize and manage .In RFID technology, EPC (Electronic Product Code) and TID (Tag Identifier) are two core concepts. For companies that want to choose and use RFID technology, an in-depth understanding of these two elements will help them more accurately customize and manage RFID systems to meet a variety of needs, from inventory management to access control. The main difference between EPC and TID is that EPC contains unique information about the products while TID gives a unique identification to each RFID tag. In RFID tag memory, three main types of data storage exist: user memory, EPC (Electronic Product Code), and TID (Tag Identification). User memory allows for storing customized data such as serial numbers, batch codes, or expiration dates.
TID Decoder. This interactive application decodes the contents of the TID bank of an EPC/RFID tag and displays the data elements it contains, following the EPC Tag Data Standard (TDS) 1.13.The v2.0.1 standard written by EPCglobal covers all RFID requirements for Gen2 RFID tags. Generally speaking, the memory of a tag is split into three: the TID, EPC, and User Memory. Tag Identifier Memory. The TID or Tag Identifier is 20 bytes or 160 bits.
mobile rfid reader access
Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security.A transponder ID (TID) is a unique number written to a transponder’s microchip by the microchip’s manufacturer. This number cannot be changed. The TID is not usually read by an RFID reader, but it is possible to create a system that authenticates the tag . An RFID tag memory is therefore divided into three parts namely the TID, the EPC, and the user memory. Some RFID tags also come with reserve memory. TID (Tag Identifier) Memory. TID memory is read-only (non-editable) and the length of TID no. is 32 to 120 bits which contains the unique identification no. of the tag manufacturer. In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about programming or encoding RFID tags including which RFID tag memory bank to use, which type of code to use - hex vs. ASCII, and how to determine how many characters you can encode.
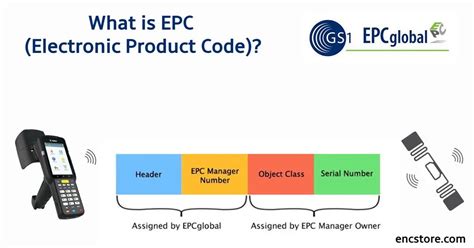
When RFID tags are placed on items for certain applications like supply chain or retail, the EPC number is encoded using an Identification Scheme. EPC Identification Schemes were created by GS1 and explain how to encode the .In RFID technology, EPC (Electronic Product Code) and TID (Tag Identifier) are two core concepts. For companies that want to choose and use RFID technology, an in-depth understanding of these two elements will help them more accurately customize and manage RFID systems to meet a variety of needs, from inventory management to access control.
The main difference between EPC and TID is that EPC contains unique information about the products while TID gives a unique identification to each RFID tag. In RFID tag memory, three main types of data storage exist: user memory, EPC (Electronic Product Code), and TID (Tag Identification). User memory allows for storing customized data such as serial numbers, batch codes, or expiration dates.TID Decoder. This interactive application decodes the contents of the TID bank of an EPC/RFID tag and displays the data elements it contains, following the EPC Tag Data Standard (TDS) 1.13.The v2.0.1 standard written by EPCglobal covers all RFID requirements for Gen2 RFID tags. Generally speaking, the memory of a tag is split into three: the TID, EPC, and User Memory. Tag Identifier Memory. The TID or Tag Identifier is 20 bytes or 160 bits.
Understand memory layout for Gen2 UHF (RAIN) RFID tags including the memory banks for EPC, User Memory, Access and TID along with key commands for security.
A transponder ID (TID) is a unique number written to a transponder’s microchip by the microchip’s manufacturer. This number cannot be changed. The TID is not usually read by an RFID reader, but it is possible to create a system that authenticates the tag .
An RFID tag memory is therefore divided into three parts namely the TID, the EPC, and the user memory. Some RFID tags also come with reserve memory. TID (Tag Identifier) Memory. TID memory is read-only (non-editable) and the length of TID no. is 32 to 120 bits which contains the unique identification no. of the tag manufacturer. In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about programming or encoding RFID tags including which RFID tag memory bank to use, which type of code to use - hex vs. ASCII, and how to determine how many characters you can encode.
what is epc data
epcglobal gen2
epc rfid gen 3

Listen to Ethno.FM 87.7 from Sacramento CA live on Radio Garden. Explore live radio by rotating the globe. Listen to Ethno.FM 87.7 from Sacramento CA live on Radio Garden. Explore live .
rfid tag epc tid|decode identifier