hf rfid chips jpeg HF RFID chips offer high data transfer rates and are commonly used in applications that . $16.99
0 · Types of RFID Chips
1 · The Ultimate Guide to NXP ICODE RFID Chips: Encryption,
2 · The Common RFID High Frequency (HF) Chips
3 · RFID Chips Selection Guide: Types, Features, Applications
4 · NXP ICODE® Chip Series: The Ultimate Guide to RFID
NFC No. 1 San Francisco 49ers 24, NFC No. 7 Green Bay Packers 21; NFC No. 3 Detroit Lions 31, No. 4 Tampa Bay Buccaneers 23; Wild Card Weekend Scores 2024. Here’s a roundup of scores and results from .
Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a .The NXP ICODE® family consists of high-frequency (HF) RFID chips that operate at 13.56 .HF RFID chips offer high data transfer rates and are commonly used in applications that .Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high-frequency (HF) RFID range. Compared to ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID, high-frequency RFID offers the following advantages: Shorter Reading Distance: Typically between 1 and 2 meters, making it more effective .
The NXP ICODE® family consists of high-frequency (HF) RFID chips that operate at 13.56 MHz and comply with ISO/IEC 15693 standards. These chips are well-known for their long-range readability, reliable anti-collision capabilities, and compatibility with various industry standards.
Previous. HF RFID chips offer high data transfer rates and are commonly used in applications that require more data storage capacity than LF RFID chips. Additionally, they have shorter read ranges compared to UHF RFID chips, making them suitable for applications where close proximity is required. NXP MIFARE Classic: This is one of the most. Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.We offer the industry’s broadest array of HF 13.56 MHz Tags, conforming to ISO 15693 and ISO 14443 parts A & B, to include FRAM memory chips from Fujitsu. We can also support older obsolete chips like the original Philips I-Code. RFID chips are categorized by frequency — Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), Ultra High Frequency (UHF), and Microwave Frequency. Higher frequencies offer extended communication ranges, with the popular 13.56 MHz HF band known for .
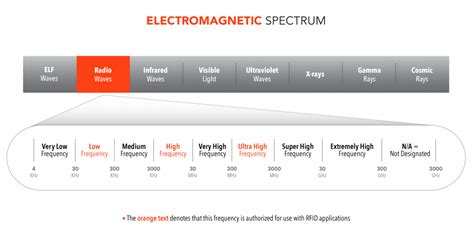
How to Decode RFID Tags (HF) Content of This Article. What Is a Tag Type? Decoding Tag Types by Default. Decoding the UID (Unique Identifier) Why Is It Important to Know the RFID Tag Type? Which Tag Types and Chip Types Are Supported by .Consists of adhesive backing with a thin printed RFID inlay antenna and chipset. Labels can be mounted directly on metal or onto standard targets. Databolts, cards, bracelets and fobs High-Frequency tags. High Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a wide range of storing capacities and . Designing a HF-RFID reader involves relatively few components, primarily the RFID reader/transceiver chip, a microcontroller, an antenna, and an interface to the IT system that processes the information received from the RFID reader.
smart card reader using mifare technology ppt
Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high-frequency (HF) RFID range. Compared to ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID, high-frequency RFID offers the following advantages: Shorter Reading Distance: Typically between 1 and 2 meters, making it more effective .The NXP ICODE® family consists of high-frequency (HF) RFID chips that operate at 13.56 MHz and comply with ISO/IEC 15693 standards. These chips are well-known for their long-range readability, reliable anti-collision capabilities, and compatibility with various industry standards.Previous. HF RFID chips offer high data transfer rates and are commonly used in applications that require more data storage capacity than LF RFID chips. Additionally, they have shorter read ranges compared to UHF RFID chips, making them suitable for applications where close proximity is required. NXP MIFARE Classic: This is one of the most.
Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.We offer the industry’s broadest array of HF 13.56 MHz Tags, conforming to ISO 15693 and ISO 14443 parts A & B, to include FRAM memory chips from Fujitsu. We can also support older obsolete chips like the original Philips I-Code. RFID chips are categorized by frequency — Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), Ultra High Frequency (UHF), and Microwave Frequency. Higher frequencies offer extended communication ranges, with the popular 13.56 MHz HF band known for .
How to Decode RFID Tags (HF) Content of This Article. What Is a Tag Type? Decoding Tag Types by Default. Decoding the UID (Unique Identifier) Why Is It Important to Know the RFID Tag Type? Which Tag Types and Chip Types Are Supported by .
Consists of adhesive backing with a thin printed RFID inlay antenna and chipset. Labels can be mounted directly on metal or onto standard targets. Databolts, cards, bracelets and fobs High-Frequency tags. High Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a wide range of storing capacities and .
Types of RFID Chips
The Ultimate Guide to NXP ICODE RFID Chips: Encryption,
smart card reader ziggo
ACR1252 Contactless Smartcard Development Kit Development kit for the ACR1252 NFC .
hf rfid chips jpeg|NXP ICODE® Chip Series: The Ultimate Guide to RFID